What materials are commonly utilized in the fabrication of ballistic helmets?
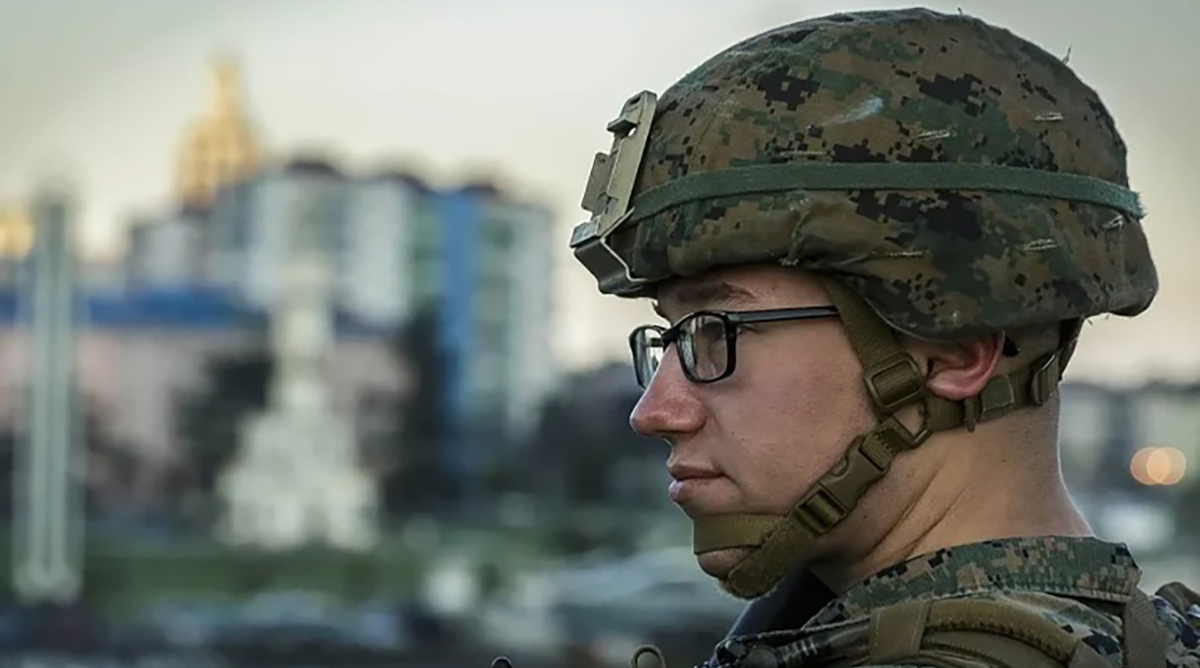

Ballistic helmets are typically constructed using a combination of specialized materials to provide protection against ballistic threats. Common materials used in the construction of ballistic helmets include:
- Aramid fibers (e.g., Kevlar): These synthetic fibers are known for their high strength-to-weight ratio and are commonly used in the production of helmets to provide protection against bullets and fragments.
- High-strength composites: Various composite materials, often reinforced with fibers such as aramid or fiberglass, are used to enhance the strength and ballistic resistance of the helmet while keeping it lightweight.
- Ceramic plates: Some ballistic helmets incorporate ceramic plates, such as boron carbide or alumina, to provide additional protection against high-velocity projectiles. These plates are usually integrated into the helmet design.
- Ballistic fabric layers: Multiple layers of specialized ballistic fabrics are often used to increase protection while maintaining flexibility and comfort. These fabrics can include aramid, UHMWPE (ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene), and other high-performance materials.
- Carbon fiber: Carbon fiber is utilized in certain helmet models to provide strength and impact resistance while minimizing weight.
- Lining and padding: Helmets feature inner linings and padding made from materials like foam or memory foam to enhance comfort, shock absorption, and impact dispersion.
The combination and design of these materials can vary among different helmet models, and they are engineered to meet specific ballistic protection standards, such as those defined by the National Institute of Justice (NIJ) or the U.S. Military’s ACH (Advanced Combat Helmet) standards, to ensure effective protection against various ballistic threats.